# Service Offerings
Services that are available for deployment via the Service Lifecycle Management are offered as so-called service offerings. A service offering can have multiple versions. After ordering a service offering, a new service instance is deployed based on the service offering and the selected version.
# Creating service offerings
There are two ways to create the service offering: Using a wizard or based on a Git repository.
# Service Offering Wizard
Go to the section Service Vendor, select the service vendor for which you want to create a new service offering, and click on the ADD SERVICE OFFERING button.
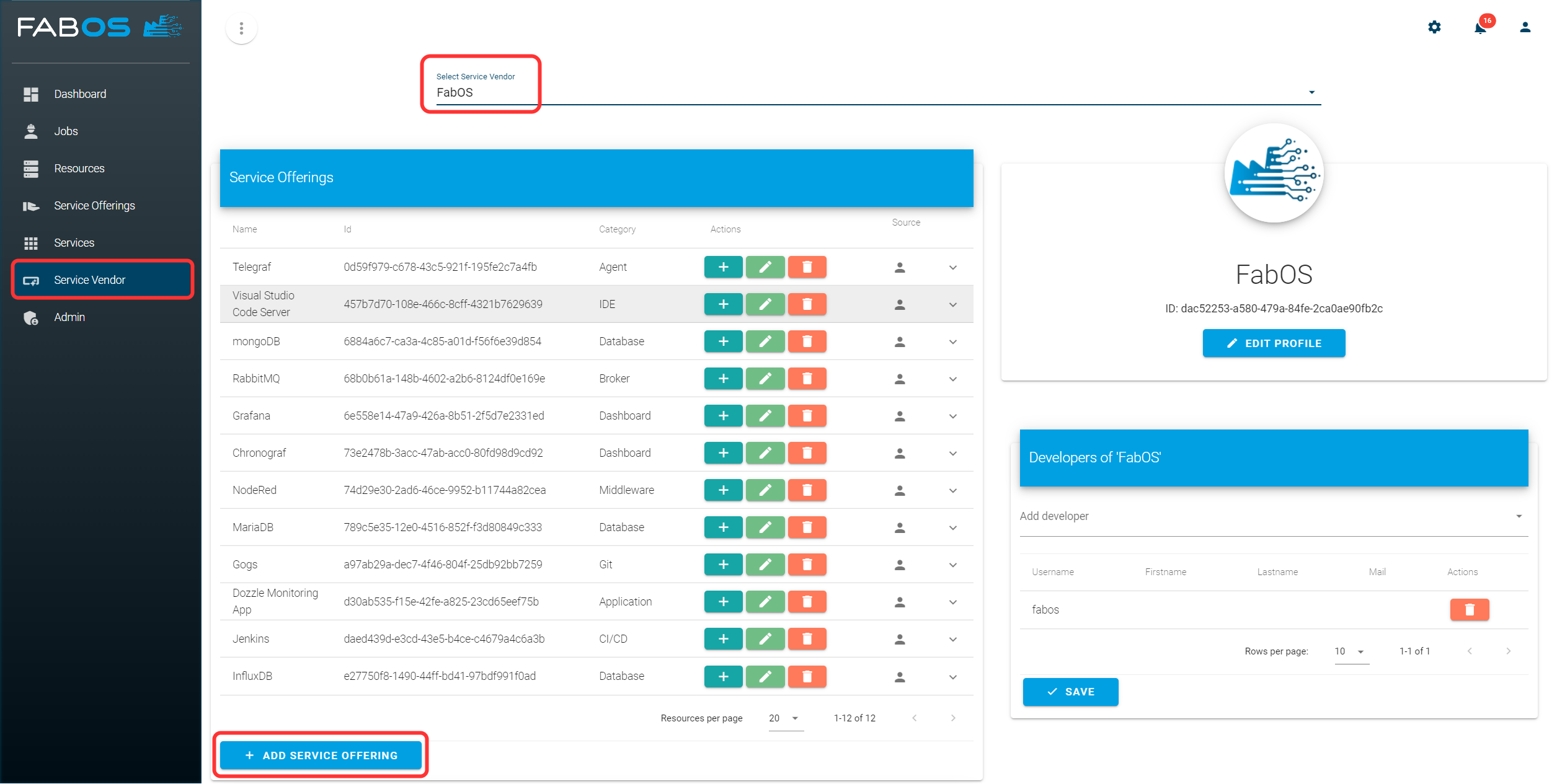
Click on SERVICE OFFERING WIZARD.
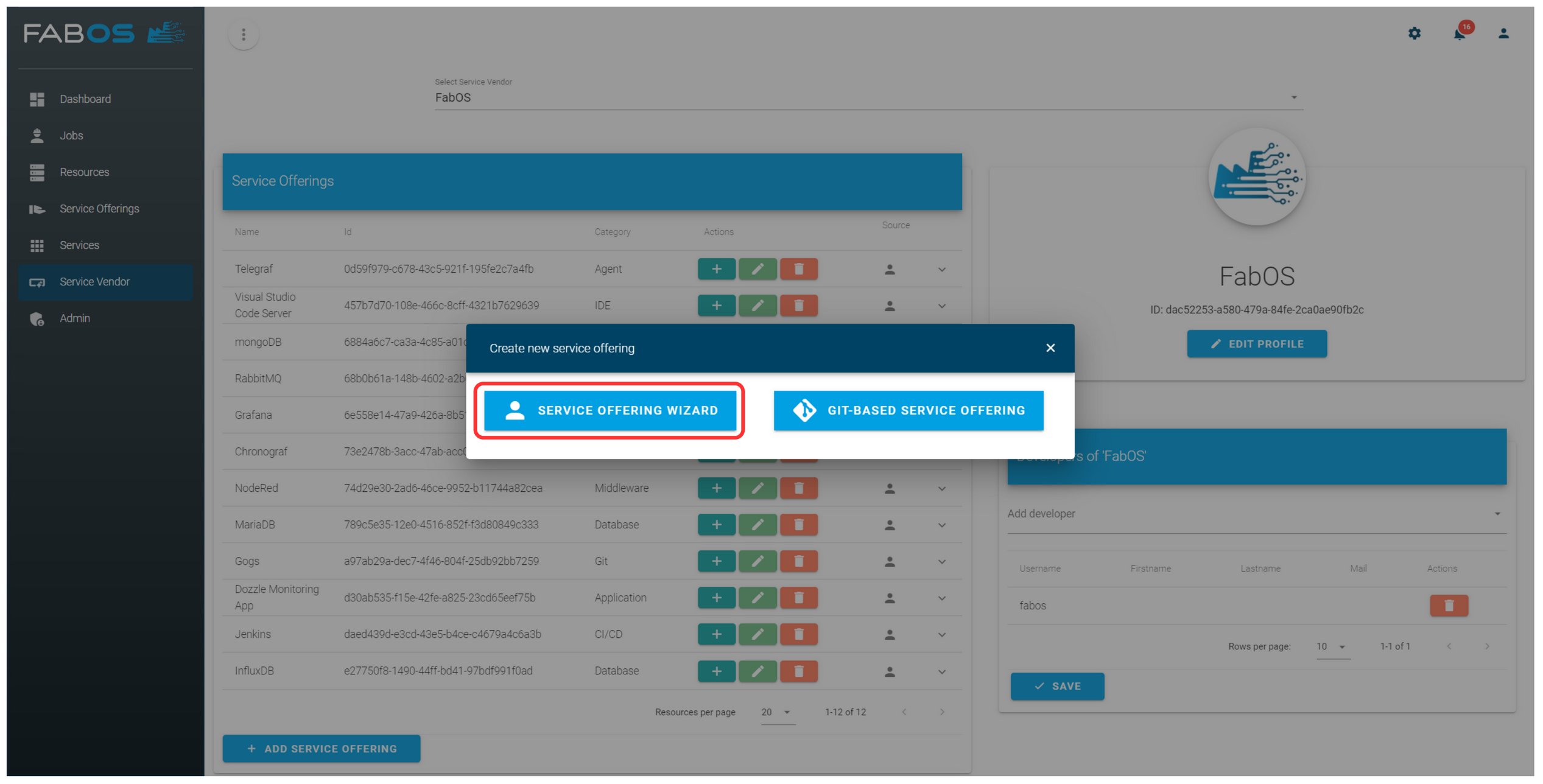
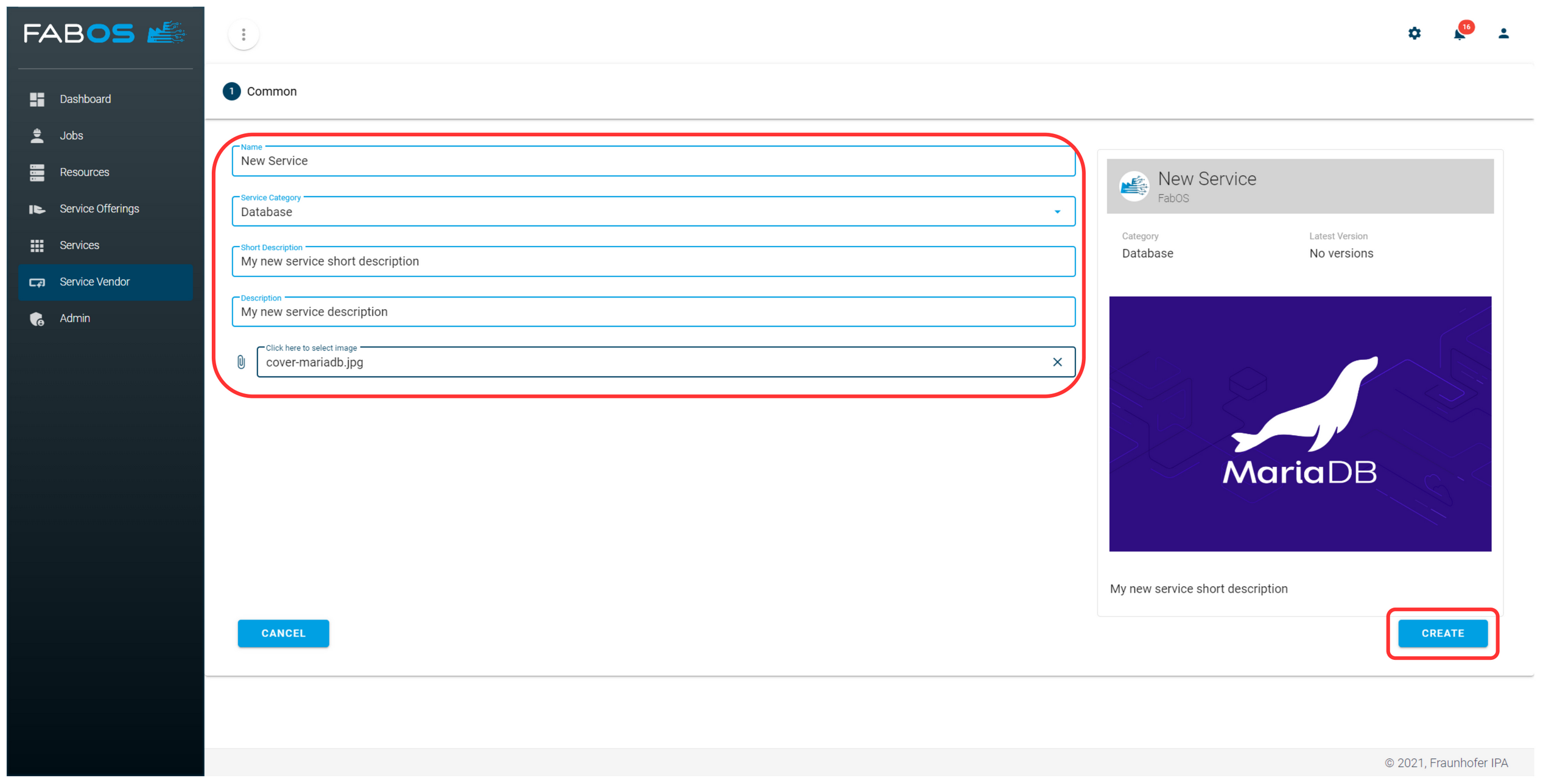
Enter the details of the new service offering and click on CREATE.
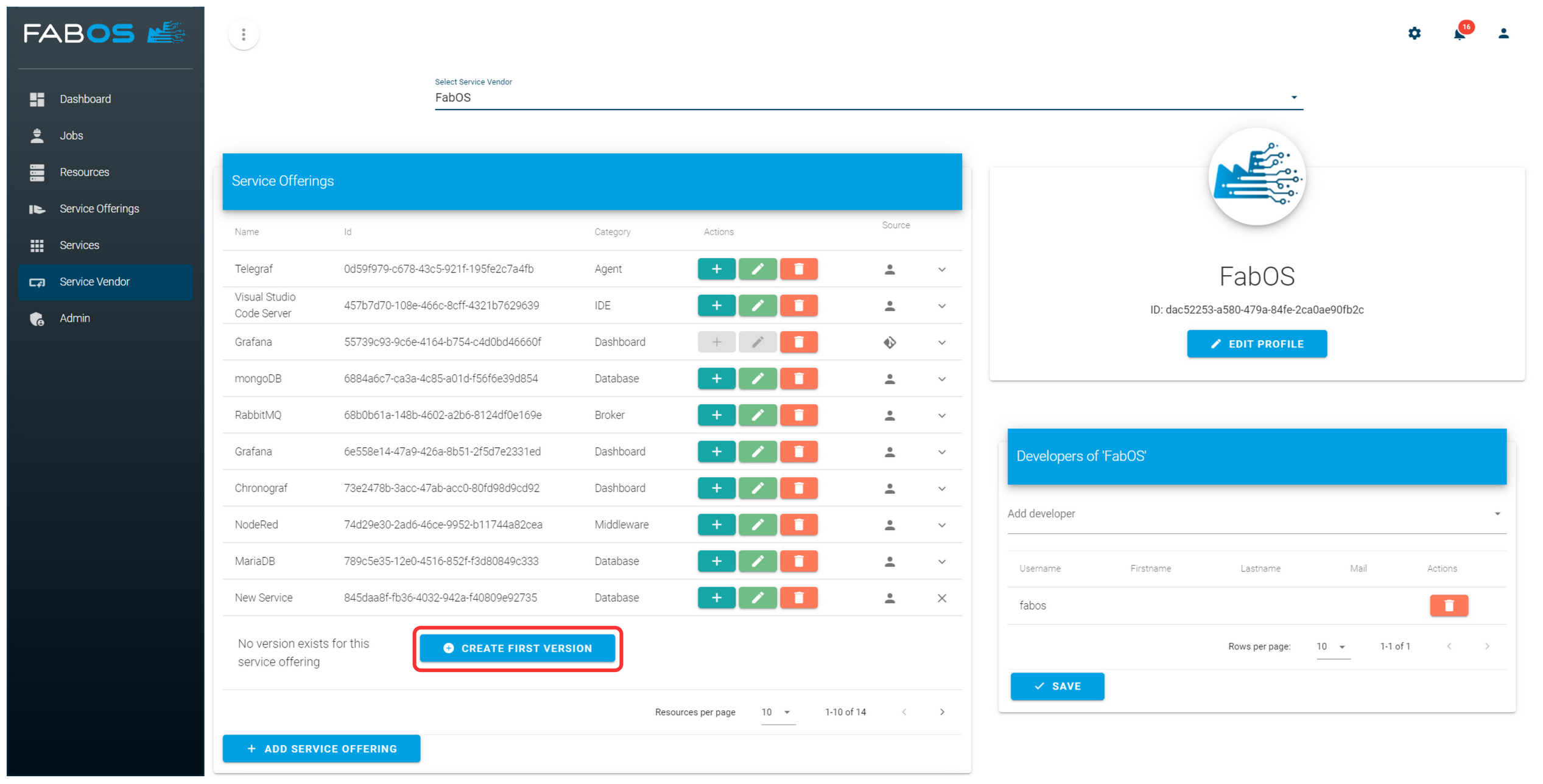
The service offering gets created and will be visible in the service offerings list of the service vendor. To be able to order a service offering, a version must be created. To do this, click in the new service offering on CREATE FIRST VERSION.
Enter the version number and select a deployment type. The following step in the wizard depends on the selected deployment type. In this case Docker Container is selected as deployment type.
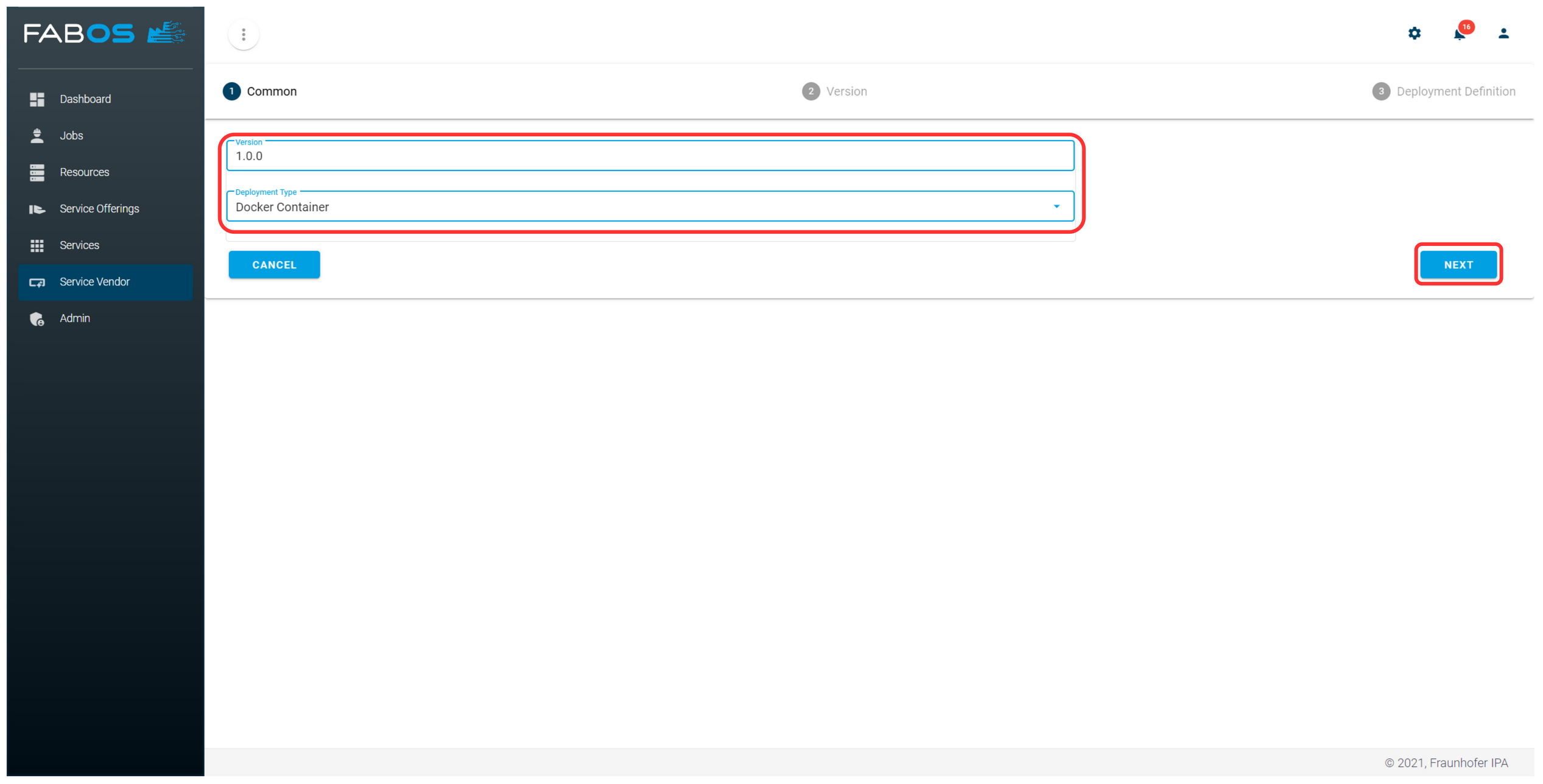
Enter the details used to deploy a Docker container based on the service offering version.
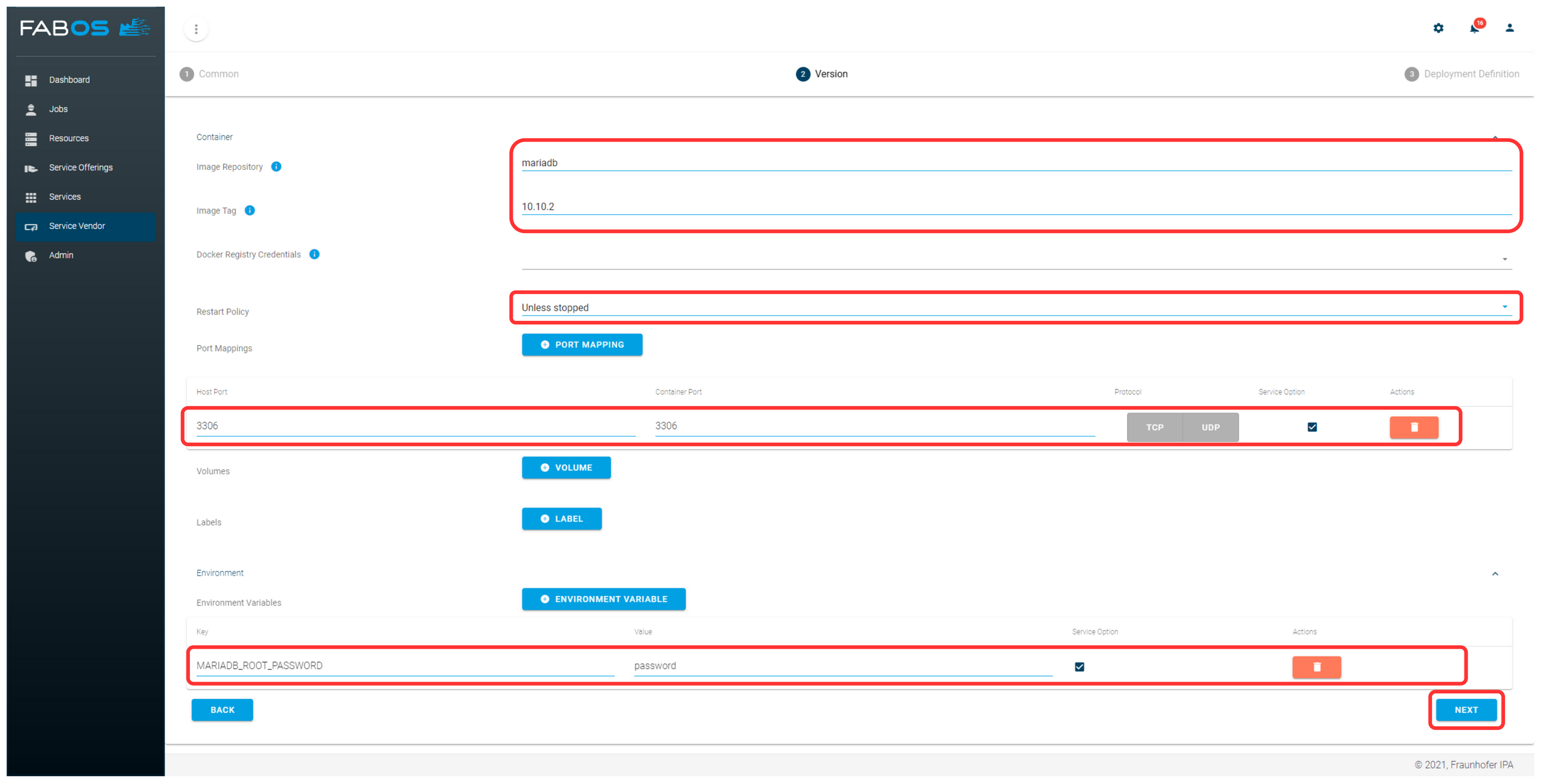
Definitions such as port mappings, volumes, labels or environment variables can be shown to the user as service options when ordering. This allows the user to configure the service instance that will be deployed. In the wizard's last step, the service options are automatically generated based on the previous step, and the service options can be configured. Further details on the service options are described here. Finally, click CREATE.
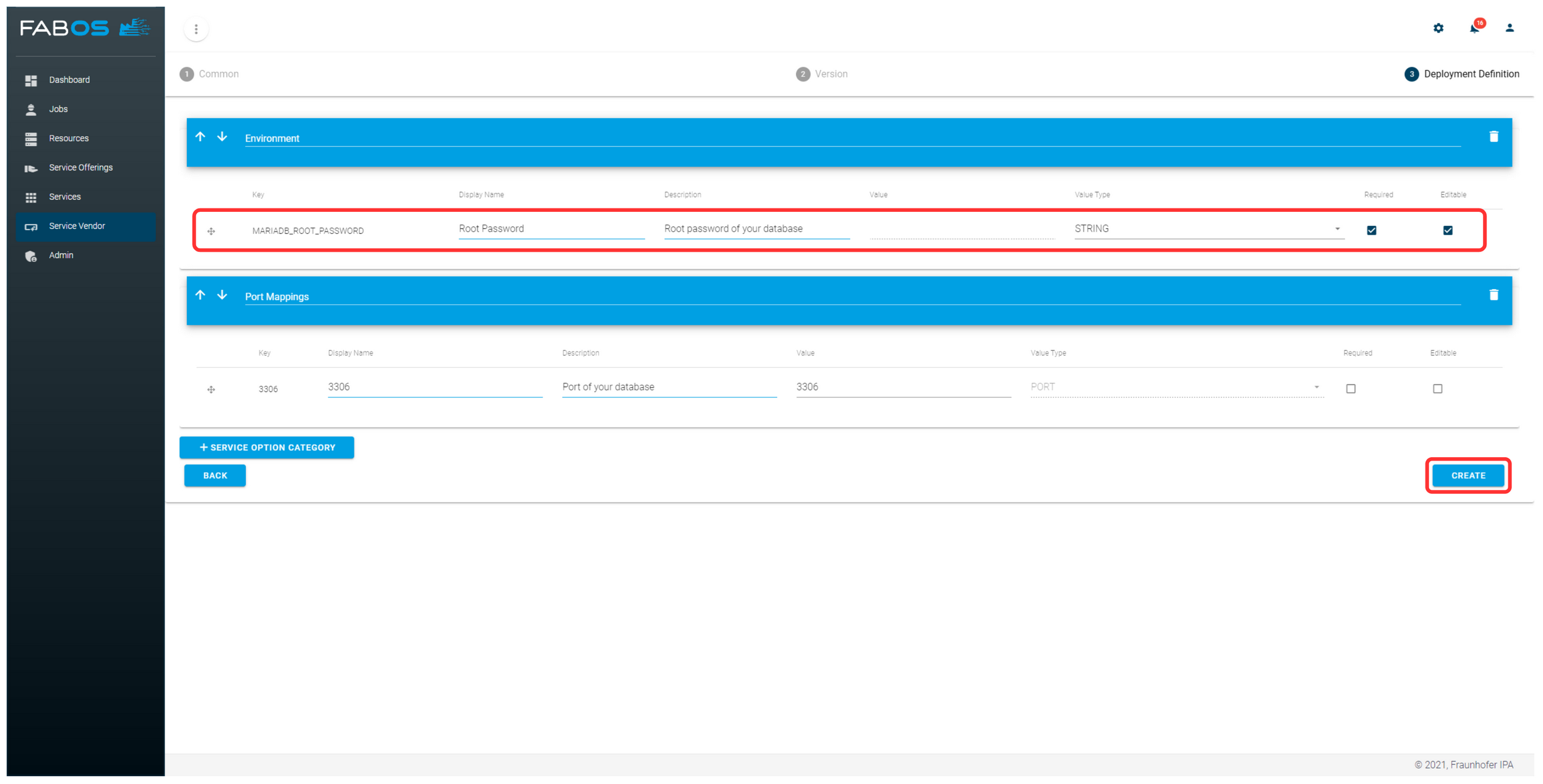
The service offering version gets created and will be shown as a version of the newly created service offering.
# Git-based service offerings
To automatically create a service offering based on a Git repository, a file named fabos.yaml must be stored in the repository. This file contains all the necessary information to describe a service offering. The file is structured as shown in the example below. Files (e.g., images, compose files, environment variable files) are referenced via their file name and the relative path to the root of the Git repository. An example is available in a public Git repository (opens new window).
name: My Service
serviceVendorId: 2eb5f19f-b75b-4bab-aa57-326320ff14ee
description: This is the long description of my service which will be shown in the
detail view of the service offering.
shortDescription: This is the short description of my service which will be shown in
the overview of all service offerings.
coverImageFilename: my-service-cover.png
serviceCategoryName: Dashboard
version:
serviceOptionCategories: []
serviceRequirements: []
serviceRepositories: []
deploymentDefinition:
deploymentType: DOCKER_COMPOSE
composeFilename: docker-compose.yml
envFilenames:
- env.list
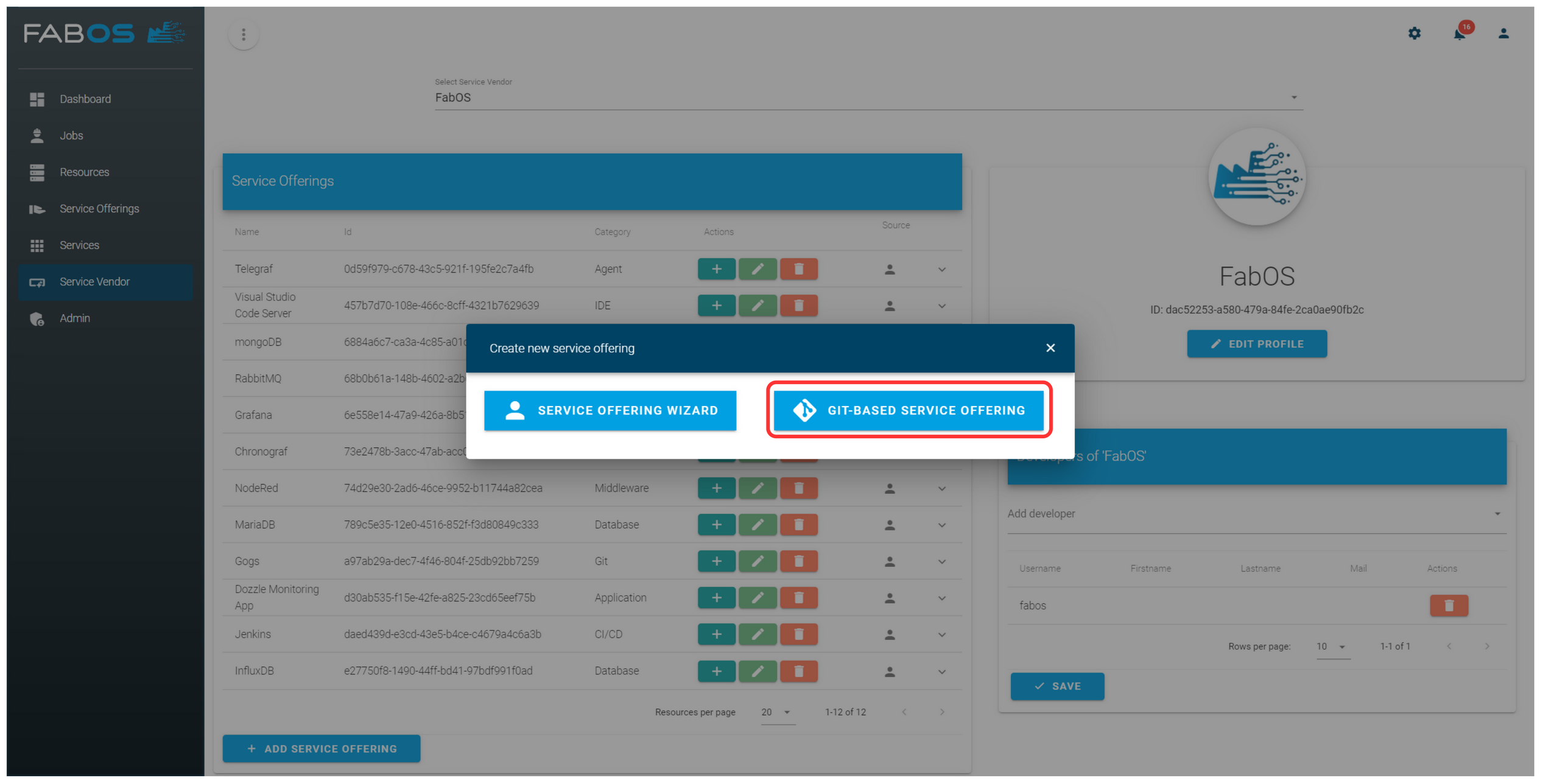
Go to the section Service Vendor, select the service vendor for which you want to create a new service offering, and click on the ADD SERVICE OFFERING button.

Click on GIT-BASED OFFERING.
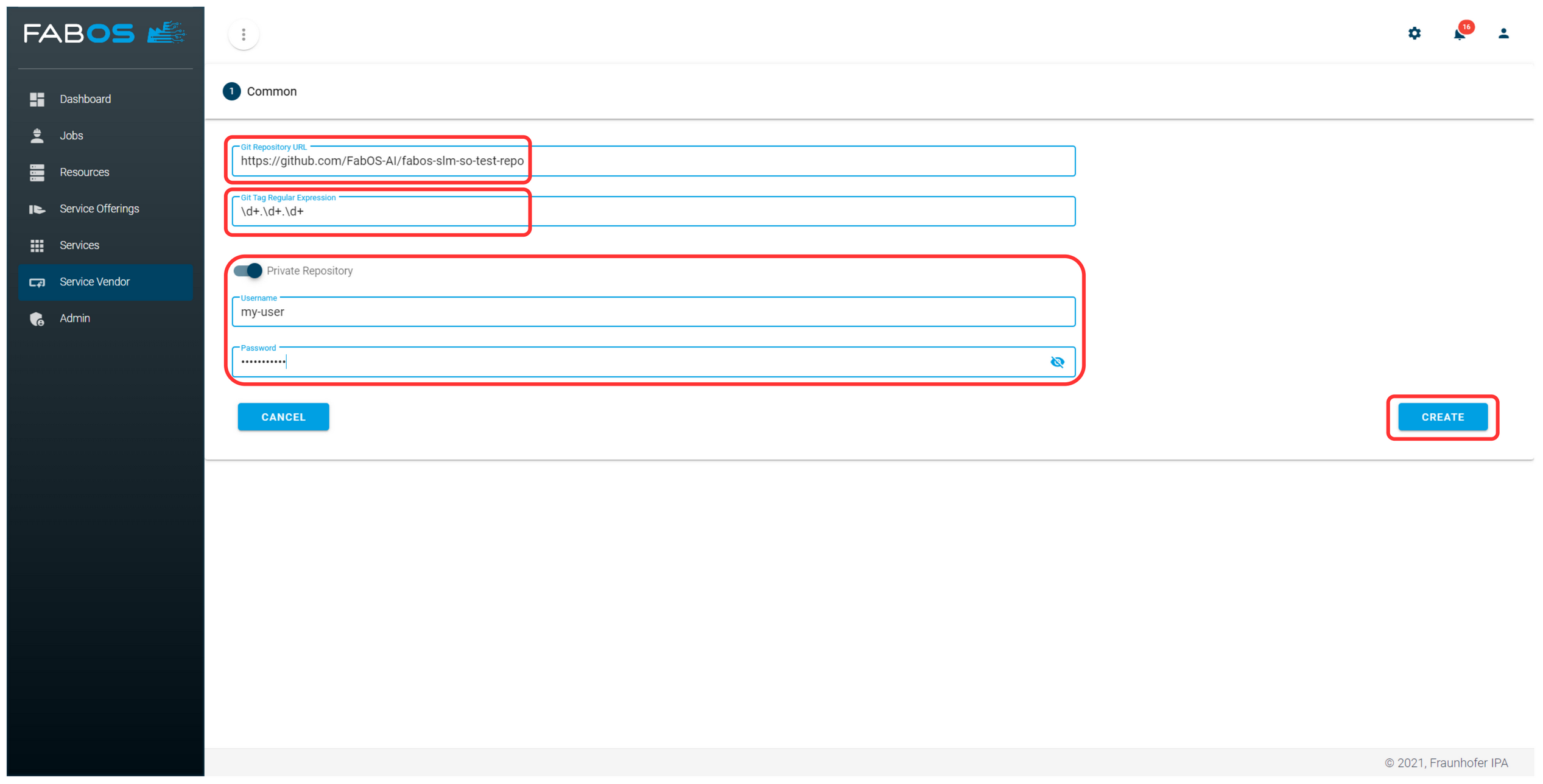
Enter the URL of the Git repository and a regular expression. All tags matching this regular expression will be created as a version of the service offering. The tag name is used as the version name. If the Git repository is private, credentials to access the Git repository must be provided. Finally, click the CREATE button.
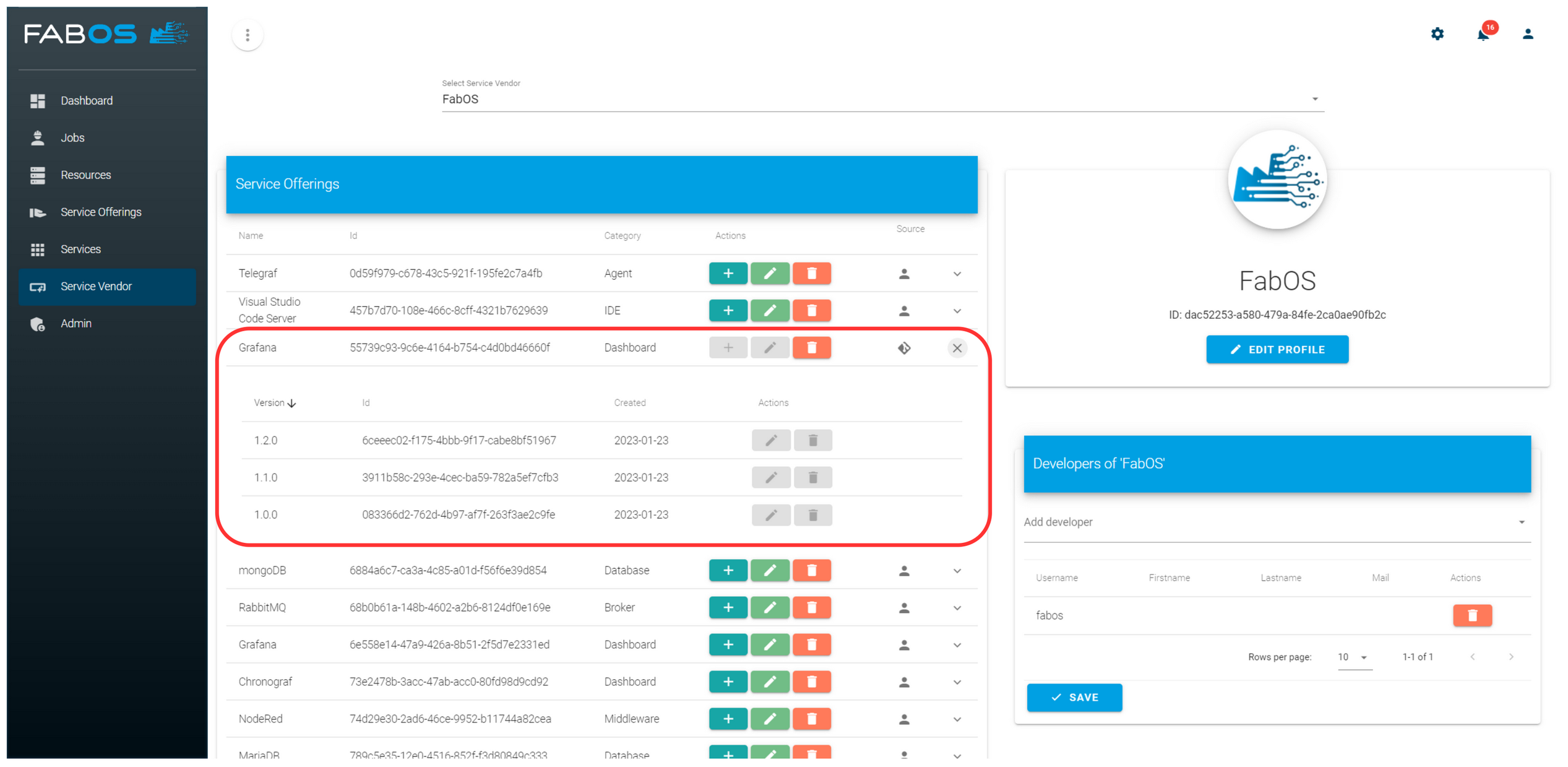
The Service Lifecycle Management analyses the repository and checks whether version tags exist. A version of the service offering is created for each existing version tag. The Git repository will be checked periodically for new tags, and, if necessary, a new service offering version will be created. The interval at which the tags of the git repository are checked can be configured via the environment variable SERVICE_REGISTRY_GIT_CHECK_INTERVAL_MINUTES in the .env file. The service offering then appears in the overview with all service offerings. For git-based service offerings, versions cannot be created or deleted manually. After a tag is deleted from the Git repository, the corresponding service offering version will also be deleted during the next check.
# Service Options
Service options allow the user to make configurations when ordering a service. The configured service options are provided service instance deployed. A service option has the following properties:
- Relation: Relation to a section in the deployment definition (e.g., a service in a docker compose file).
- Key: Key to identify the service option.
- Name: Name of the service option.
- Description: Description of the service option.
- Option Type: Type of the service option. Possible types are:
- ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLE
- PORT_MAPPING
- VOLUME
- LABEL
- Default Value: The default value of the service option.
- Value Type: The value type is mainly used for how the input fields are queried from the user during an order of a service offering. Possible value types are:
| Value Type | Description |
|---|---|
| STRING | Input field for plain text |
| PASSWORD | Input field for plain text. The text is masked. |
| BOOLEAN | Boolean value with checkbox as input. |
| NUMBER | Integer or decimal numbers. |
| INTEGER | Integer numbers. |
| DECIMAL | Decimal numbers. |
| Input field with format check for email addresses. | |
| IP | Input field with format check for IPv4 addresses. |
| ENUM | Dropdown with values from Value Options as elements. |
| AUTO_GENERATED_UUID | A UUID is generated automatically. |
| PORT | Port in the range from 0 to 65535 |
| VOLUME | Input field with format check for volumes. |
| AAS_SM_TEMPLATE | The semantic ID of a Asset Administration Shell (AAS) submodel can be defined. When the user orders the service offering, all AAS that have an instance of this submodel are searched in the AAS register. The result is presented to the user as a dropdown list. |
| TEMPLATE_VARIABLE | Common variables provided by the service registry (e.g., values from application properties) |
- Value Options: Possible options for values which the user can choose. Currently only relevant for Value Type
ENUM. - Required: If set to
true, the user will be forced to make an input when ordering the service offering. - Editable: If set to
true, the user can change the default value when ordering the service offering. If set tofalse. The default value is visible (read-only) for the user.
The service options of a service offering are organized into service option categories. A service option category consists of an id, a name and a list of service options.
Example for service categories definition:
serviceOptionCategories:
- id: 0
name: Light
serviceOptions:
- relation: env.list
key: COLOR
name: "Color"
description: 'The color to be displayed. Valid colors are: red, green, blue'
optionType: ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLE
defaultValue: blue
valueType: ENUM
valueOptions:
- red
- green
- blue
required: true
editable: true
- relation: env.list
key: BRIGHTNESS
name: "Brightness"
description: 'The brightness to be displayed \nValid brightness values are: [0 up to 100]'
optionType: ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLE
defaultValue: 99
valueType: INTEGER
valueOptions: []
required: true
editable: true
- relation: env.list
key: EFFECT
name: "Animation Effect"
description: 'The animation effect to be displayed \nValid effects are: solid, blink, breath'
optionType: ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLE
defaultValue: rainbow
valueType: ENUM
valueOptions:
- solid
- blink
- breath
required: true
editable: true
- id: 1
name: Connection
serviceOptions:
- relation: env.list
key: MSB_HOST
name: The Host of the running MSB stack, preferably as IP
description: The Host of the running MSB stack
optionType: ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLE
defaultValue: 192.168.153.46
valueType: STRING
valueOptions: []
required: true
editable: true
- relation: env.list
key: MSB_UUID
name: The UUID for the WS client of the MSB
description: The UUID for the WS client of the MSB
optionType: ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLE
defaultValue: a5d2fbeb-bac5-4269-90ee-6813491734b5
valueType: STRING
valueOptions: []
required: true
editable: true
